Connect to the Kafka from Java app
Start environment
Run Kafka broker described in previous post.
Create java project
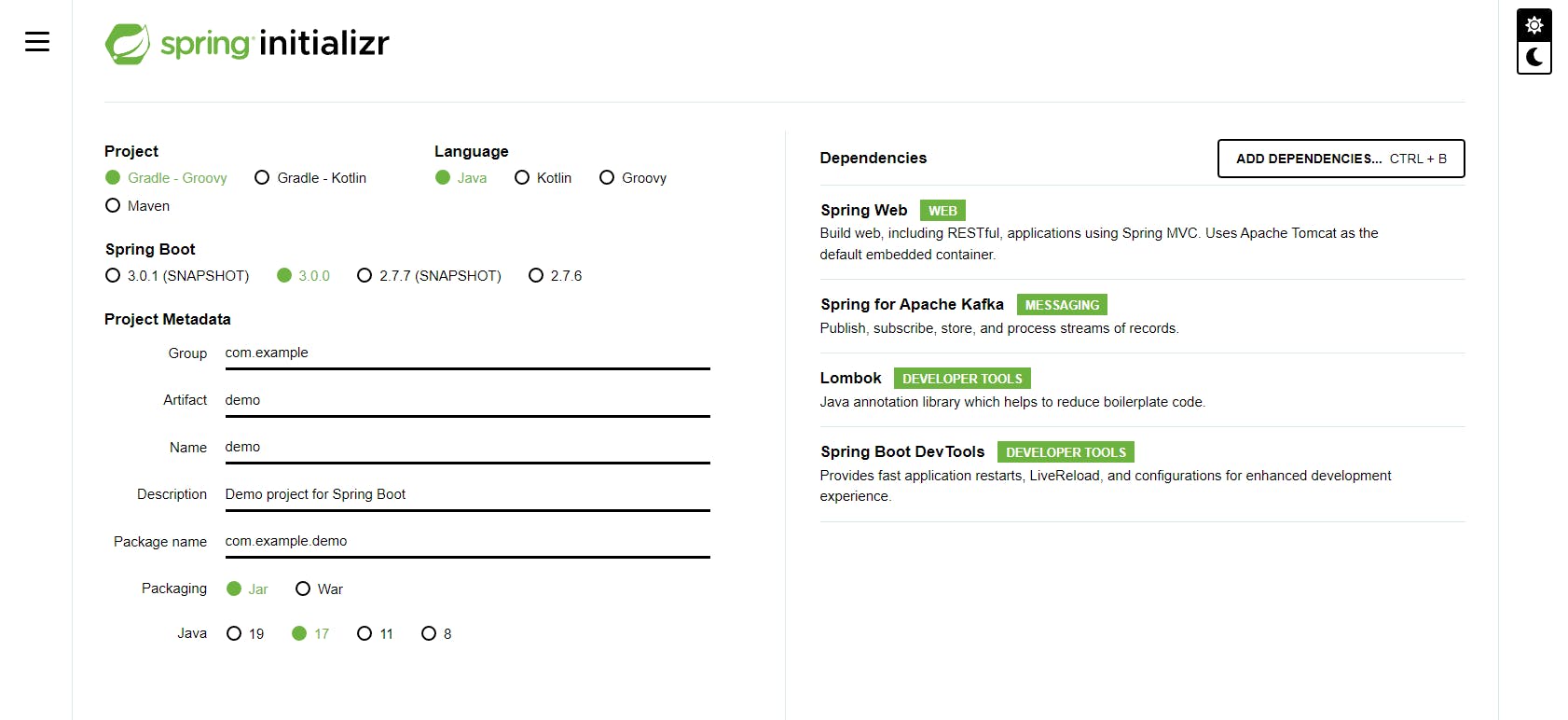
You can use Spring Initializr for creating a new project. Add required dependencies (no all will be used in this part, but will be useful in short future).
- Spring Web - Build web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Apache Tomcat as the default embedded container.
- Spring for Apache Kafka - Publish, subscribe, store, and process streams of records.
- Lombok - Java annotation library which helps to reduce boilerplate code.
- Spring Boot DevTools - Provides fast application restarts, LiveReload, and configurations for enhanced development experience.
Kafka Configuration
We will start from creating Kafka configuration. Put your attention on annotation EnableKafka.
package and import (for local files) lines were removed, because you will have different hierarchy.
import org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.ConsumerConfig;
import org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.EnableKafka;
import org.springframework.kafka.config.ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.ConsumerFactory;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@EnableKafka
@Configuration
public class KafkaConfig {
@Value(value = "${spring.kafka.consumer.bootstrap-servers}")
private String bootstrapAddress;
@Value(value = "${spring.kafka.consumer.group-id}")
private String groupId;
@Bean
public ConsumerFactory<String, String> consumerFactory() {
Map<String, Object> props = new HashMap<>();
props.put(ConsumerConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, bootstrapAddress);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, groupId);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.KEY_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
props.put(ConsumerConfig.VALUE_DESERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG, StringDeserializer.class);
return new DefaultKafkaConsumerFactory<>(props);
}
@Bean
public ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, String> kafkaListenerContainerFactory() {
ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<String, String> factory =
new ConcurrentKafkaListenerContainerFactory<>();
factory.setConsumerFactory(consumerFactory());
return factory;
}
}
Kafka consumer
import org.springframework.kafka.annotation.KafkaListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class KafkaConsumerService {
@KafkaListener(topics = "testtopic")
public void listenTopic(String message){
System.out.println("Received Message from topic: " + message);
}
}
Start spring boot application from your IDE. Send a message to testtopic and log should be seen in run console.
Kafka producer
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.kafka.support.SendResult;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFuture;
import org.springframework.util.concurrent.ListenableFutureCallback;
@Component
public class KafkaProducerService {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
public void sendMessage(String topic, String message) {
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String, String>> future =
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, message);
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback<SendResult<String, String>>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(SendResult<String, String> result) {
System.out.println("Sent message=[" + message +
"] with offset=[" + result.getRecordMetadata().offset() + "]");
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("Unable to send message=["
+ message + "] due to : " + ex.getMessage());
}
});
}
}
Test producer
For quick test if we can send a message from our app to the Kafka topic we will create one REST endpoint.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("kafka/producer")
public class KafkaProducerController {
@Autowired
private KafkaProducerService producerService;
@GetMapping("/{topic}/{msg}")
public void sendMessageToKafka(@PathVariable String topic, @PathVariable String msg){
producerService.sendMessage(topic, msg);
}
}
Restart your application. In the browser execute eg. URL:
http://localhost:8080/kafka/producer/testtopic/testMessage
As a result testMessage should be shown in the logs, because KafkaConsumerService is up and running.